Данный пост показывает отношение многие-ко-многим в Hibernate, на примере соединения таблиц в веб-приложении Spring 4 MVC. Мы будем обсуждать управление отношением многие-ко-многим в представлениях и в бэк-энд’ах. Мы выполним операции создания, обновления, удаления и запрос через веб-интерфейс.
Это приложение использует интерфейс org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter, который помогает нам в отображении ID’ предметов в настоящих субъектах в базе данных.
Были использованы следующие технологии:
- Spring 4.1.7.RELEASE
- Hibernate Core 4.3.10.Final
- validation-api 1.1.0.Final
- hibernate-validator 5.1.3.Final
- MySQL Server 5.6
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.7
- NetBeans 8.0.2
Приступим.
Шаг 1: Создадим схему для отношения многие-ко-многим с использованием JOIN table

APP_USER: Содержит пользователей. Пользователь может иметь несколько профилей [USER,ADMIN,DBA].
USER_PROFILE: Содержит профили пользователей. Профиль может быть связан с несколькими пользователями.
APP_USER_USER_PROFILE: Это соединяющая таблица, которая связывает таблицы APP_USER и USER_PROFILE с отношением многие-ко-многим.
В демонстрационных целях, мы будем обсуждать отношение многие-ко-многим в однонаправленной установке [пользователь с профилем пользователя] в этом примере.
create table APP_USER ( id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, sso_id VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, password VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, first_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, last_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id), UNIQUE (sso_id) ); create table USER_PROFILE( id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, type VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id), UNIQUE (type) ); CREATE TABLE APP_USER_USER_PROFILE ( user_id BIGINT NOT NULL, user_profile_id BIGINT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (user_id, user_profile_id), CONSTRAINT FK_APP_USER FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES APP_USER (id), CONSTRAINT FK_USER_PROFILE FOREIGN KEY (user_profile_id) REFERENCES USER_PROFILE (id) ); /* Populate USER_PROFILE Table */ INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type) VALUES ('USER'); INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type) VALUES ('ADMIN'); INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type) VALUES ('DBA'); commit;
Шаг 2: Создаем структуру каталога
Финальная структура проекта будет выглядеть следующим образом.

Шаг 3: Обновление pom.xml, чтобы включить нужные зависимости
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.websystique.springmvc</groupId> <artifactId>SpringMVCHibernateManyToManyCRUDExample</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0.0</version> <name>SpringMVCHibernateManyToManyCRUDExample</name> <properties> <springframework.version>4.1.7.RELEASE</springframework.version> <hibernate.version>4.3.10.Final</hibernate.version> <mysql.connector.version>5.1.31</mysql.connector.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- Spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>${springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Hibernate --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>${hibernate.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- jsr303 validation --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> <artifactId>validation-api</artifactId> <version>1.1.0.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>5.1.3.Final</version> </dependency> <!-- MySQL --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${mysql.connector.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Servlet+JSP+JSTL --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <pluginManagement> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.4</version> <configuration> <warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory> <warName>SpringMVCHibernateManyToManyCRUDExample</warName> <failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> <finalName>SpringMVCHibernateManyToManyCRUDExample</finalName> </build> </project>
Шаг 4: Подготовка модельных классов
package com.websystique.springmvc.model; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.JoinTable; import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import javax.persistence.Table; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty; @Entity @Table(name="APP_USER") public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id; @NotEmpty @Column(name="SSO_ID", unique=true, nullable=false) private String ssoId; @NotEmpty @Column(name="PASSWORD", nullable=false) private String password; @NotEmpty @Column(name="FIRST_NAME", nullable=false) private String firstName; @NotEmpty @Column(name="LAST_NAME", nullable=false) private String lastName; @NotEmpty @Column(name="EMAIL", nullable=false) private String email; @NotEmpty @ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @JoinTable(name = "APP_USER_USER_PROFILE", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "USER_ID") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "USER_PROFILE_ID") }) private Set<UserProfile> userProfiles = new HashSet<UserProfile>(); public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getSsoId() { return ssoId; } public void setSsoId(String ssoId) { this.ssoId = ssoId; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public Set<UserProfile> getUserProfiles() { return userProfiles; } public void setUserProfiles(Set<UserProfile> userProfiles) { this.userProfiles = userProfiles; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((ssoId == null) ? 0 : ssoId.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (!(obj instanceof User)) return false; User other = (User) obj; if (id == null) { if (other.id != null) return false; } else if (!id.equals(other.id)) return false; if (ssoId == null) { if (other.ssoId != null) return false; } else if (!ssoId.equals(other.ssoId)) return false; return true; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", ssoId=" + ssoId + ", password=" + password + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + "]"; } }
Посмотрите, как свойство userProfiles аннотируется c «многие-ко-многим».
@ManyToMany указывает, что есть отношение многие-ко-многим между пользователем и профилем пользователя. Пользователь может иметь несколько профилей [USER, ADMIN, DBA], в то время как, профиль может принадлежать нескольким пользователям.@JoinTable показывает, что есть ссылочная таблица, которая соединяет две таблицы, используя ограничения внешних ключей к их первичным. Эта аннотация в основном используется на стороне владеющей отношений. joinColumns ссылается к имени столбца на владеющей стороне (ID пользователя), а обратная joinColumns относится к колонке обратной стороны отношения (ID и профиль пользователя). Первичный ключ этой соединяющей таблицы есть сочетание USER_ID и USER_PROFILE_ID.
«Ленивая загрузка»
Обратите особое внимание на fetch = FetchType.LAZY.Здесь мы информируем Hibernate о «ленивой» загрузки коллекции userProfile. Данное поведение является основным. С такой установкой, запрос для загрузки коллекции будет удален, как только он впервые обратиться. Это хороший способ, чтобы избежать извлечения всех подключений объектов к графу, которая является «дорогой» операцией. Когда вы находитесь в транзакции / активной сессии, и будите пытаться получить доступ к коллекции, Hibernate будет отделять запросы для получения их.
Но если вы находитесь вне активной сессии (например сессия была закрыта / нет транзакций: вы находитесь на JSP странице), и попытались получить доступ к коллекции, вы встретитесь с org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException – could not initialize proxy – no Session. Чтобы избежать этого, вы должны инициализировать коллекцию по требованию вызовов Hibernate.initialize(user.getUserProfiles()); в активном сеансе.
Также обратите внимание, что мы не используем каскад. Это потому-что профиль пользователя не зависит от пользователя и может существовать отдельно.
Одно важное замечание: В случаи «много» ассоциаций, всегда переопределяйте методы hashCode() и equals(), которые наблюдаются Hibernate’ом при проведении сущностей в коллекции.
Класс UserProfile
package com.websystique.springmvc.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="USER_PROFILE") public class UserProfile { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id; @Column(name="TYPE", length=15, unique=true, nullable=false) private String type = UserProfileType.USER.getUserProfileType(); public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((type == null) ? 0 : type.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (!(obj instanceof UserProfile)) return false; UserProfile other = (UserProfile) obj; if (id == null) { if (other.id != null) return false; } else if (!id.equals(other.id)) return false; if (type == null) { if (other.type != null) return false; } else if (!type.equals(other.type)) return false; return true; } @Override public String toString() { return "UserProfile [id=" + id + ", type=" + type + "]"; } } Так как мы показываем однонаправленное отношение (пользователя к профилю пользователя), то нет необходимости ссылаться на пользователя в профиле пользователя.
UserProfileType
package com.websystique.springmvc.model; public enum UserProfileType { USER("USER"), DBA("DBA"), ADMIN("ADMIN"); String userProfileType; private UserProfileType(String userProfileType){ this.userProfileType = userProfileType; } public String getUserProfileType(){ return userProfileType; } }
Шаг 5: Создания слоя DAO
Интерфейс UserDao
package com.websystique.springmvc.dao; import java.util.List; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; public interface UserDao { User findById(int id); User findBySSO(String sso); void save(User user); void deleteBySSO(String sso); List<User> findAllUsers(); } Интерфейс UserProfileDao
package com.websystique.springmvc.dao; import java.util.List; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; public interface UserProfileDao { List<UserProfile> findAll(); UserProfile findByType(String type); UserProfile findById(int id); } Абстрактный класс AbstractDao
package com.websystique.springmvc.dao; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType; import org.hibernate.Criteria; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; public abstract class AbstractDao<PK extends Serializable, T> { private final Class<T> persistentClass; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public AbstractDao(){ this.persistentClass =(Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass ()).getActualTypeArguments()[1]; } @Autowired private SessionFactory sessionFactory; protected Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public T getByKey(PK key) { return (T) getSession().get(persistentClass, key); } public void persist(T entity) { getSession().persist(entity); } public void delete(T entity) { getSession().delete(entity); } protected Criteria createEntityCriteria(){ return getSession().createCriteria(persistentClass); } } Класс UserDaoImpl
package com.websystique.springmvc.dao; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Criteria; import org.hibernate.Hibernate; import org.hibernate.criterion.Order; import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; @Repository("userDao") public class UserDaoImpl extends AbstractDao<Integer, User> implements UserDao { public User findById(int id) { User user = getByKey(id); if(user!=null){ Hibernate.initialize(user.getUserProfiles()); } return user; } public User findBySSO(String sso) { System.out.println("SSO : "+sso); Criteria crit = createEntityCriteria(); crit.add(Restrictions.eq("ssoId", sso)); User user = (User)crit.uniqueResult(); if(user!=null){ Hibernate.initialize(user.getUserProfiles()); } return user; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public List<User> findAllUsers() { Criteria criteria = createEntityCriteria().addOrder(Order.asc("firstName")); criteria.setResultTransformer(Criteria.DISTINCT_ROOT_ENTITY);//To avoid duplicates. List<User> users = (List<User>) criteria.list(); return users; } public void save(User user) { persist(user); } public void deleteBySSO(String sso) { Criteria crit = createEntityCriteria(); crit.add(Restrictions.eq("ssoId", sso)); User user = (User)crit.uniqueResult(); delete(user); } } Класс UserProfileDaoImpl
package com.websystique.springmvc.dao; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Criteria; import org.hibernate.criterion.Order; import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; @Repository("userProfileDao") public class UserProfileDaoImpl extends AbstractDao<Integer, UserProfile>implements UserProfileDao{ public UserProfile findById(int id) { return getByKey(id); } public UserProfile findByType(String type) { Criteria crit = createEntityCriteria(); crit.add(Restrictions.eq("type", type)); return (UserProfile) crit.uniqueResult(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public List<UserProfile> findAll(){ Criteria crit = createEntityCriteria(); crit.addOrder(Order.asc("type")); return (List<UserProfile>)crit.list(); } }
Шаг 6: Создание сервисного слоя
Интерфейс UserProfileService
package com.websystique.springmvc.service; import java.util.List; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; public interface UserProfileService { UserProfile findById(int id); UserProfile findByType(String type); List<UserProfile> findAll(); }
Интерфейс UserService
package com.websystique.springmvc.service; import java.util.List; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; public interface UserService { User findById(int id); User findBySSO(String sso); void saveUser(User user); void updateUser(User user); void deleteUserBySSO(String sso); List<User> findAllUsers(); boolean isUserSSOUnique(Integer id, String sso); } Класс UserProfileServiceImpl
package com.websystique.springmvc.service; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.websystique.springmvc.dao.UserProfileDao; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; @Service("userProfileService") @Transactional public class UserProfileServiceImpl implements UserProfileService{ @Autowired UserProfileDao dao; public UserProfile findById(int id) { return dao.findById(id); } public UserProfile findByType(String type){ return dao.findByType(type); } public List<UserProfile> findAll() { return dao.findAll(); } } Класс UserServiceImpl
package com.websystique.springmvc.service; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.websystique.springmvc.dao.UserDao; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; @Service("userService") @Transactional public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired private UserDao dao; public User findById(int id) { return dao.findById(id); } public User findBySSO(String sso) { User user = dao.findBySSO(sso); return user; } public void saveUser(User user) { dao.save(user); } /* * Since the method is running with Transaction, No need to call hibernate update explicitly. * Just fetch the entity from db and update it with proper values within transaction. * It will be updated in db once transaction ends. */ public void updateUser(User user) { User entity = dao.findById(user.getId()); if(entity!=null){ entity.setSsoId(user.getSsoId()); entity.setPassword(user.getPassword()); entity.setFirstName(user.getFirstName()); entity.setLastName(user.getLastName()); entity.setEmail(user.getEmail()); entity.setUserProfiles(user.getUserProfiles()); } } public void deleteUserBySSO(String sso) { dao.deleteBySSO(sso); } public List<User> findAllUsers() { return dao.findAllUsers(); } public boolean isUserSSOUnique(Integer id, String sso) { User user = findBySSO(sso); return ( user == null || ((id != null) && (user.getId() == id))); } }
Шаг 7: Создание настроек Hibernate
Класс HibernateConfiguration
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration; import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; @Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @ComponentScan({ "com.websystique.springmvc.configuration" }) @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:application.properties" }) public class HibernateConfiguration { @Autowired private Environment environment; @Bean public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() { LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean(); sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource()); sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { "com.websystique.springmvc.model" }); sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties()); return sessionFactory; } @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.driverClassName")); dataSource.setUrl(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.url")); dataSource.setUsername(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.username")); dataSource.setPassword(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.password")); return dataSource; } private Properties hibernateProperties() { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.put("hibernate.dialect", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect")); properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql")); properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql")); return properties; } @Bean @Autowired public HibernateTransactionManager transactionManager(SessionFactory s) { HibernateTransactionManager txManager = new HibernateTransactionManager(); txManager.setSessionFactory(s); return txManager; } } Настройки для Hibernate:
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/таблица jdbc.username = пользователь jdbc.password = пароль hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.show_sql = true hibernate.format_sql = true
Шаг 8: Создание контроллера
package com.websystique.springmvc.controller; import java.util.List; import java.util.Locale; import javax.validation.Valid; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.MessageSource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult; import org.springframework.validation.FieldError; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; import com.websystique.springmvc.service.UserProfileService; import com.websystique.springmvc.service.UserService; @Controller @RequestMapping("/") @SessionAttributes("roles") public class AppController { @Autowired UserService userService; @Autowired UserProfileService userProfileService; @Autowired MessageSource messageSource; /** * This method will list all existing users. */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET) public String listUsers(ModelMap model) { List<User> users = userService.findAllUsers(); model.addAttribute("users", users); return "userslist"; } /** * This method will provide the medium to add a new user. */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/newuser" }, method = RequestMethod.GET) public String newUser(ModelMap model) { User user = new User(); model.addAttribute("user", user); model.addAttribute("edit", false); return "registration"; } /** * This method will be called on form submission, handling POST request for * saving user in database. It also validates the user input */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/newuser" }, method = RequestMethod.POST) public String saveUser(@Valid User user, BindingResult result, ModelMap model) { if (result.hasErrors()) { return "registration"; } /* * Preferred way to achieve uniqueness of field [sso] should be implementing custom @Unique annotation * and applying it on field [sso] of Model class [User]. * * Below mentioned peace of code [if block] is to demonstrate that you can fill custom errors outside the validation * framework as well while still using internationalized messages. * */ if(!userService.isUserSSOUnique(user.getId(), user.getSsoId())){ FieldError ssoError =new FieldError("user","ssoId",messageSource.getMessage("non.unique.ssoId", new String[]{user.getSsoId()}, Locale.getDefault())); result.addError(ssoError); return "registration"; } userService.saveUser(user); model.addAttribute("success", "User " + user.getFirstName() + " "+ user.getLastName() + " registered successfully"); //return "success"; return "registrationsuccess"; } /** * This method will provide the medium to update an existing user. */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{ssoId}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET) public String editUser(@PathVariable String ssoId, ModelMap model) { User user = userService.findBySSO(ssoId); model.addAttribute("user", user); model.addAttribute("edit", true); return "registration"; } /** * This method will be called on form submission, handling POST request for * updating user in database. It also validates the user input */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{ssoId}" }, method = RequestMethod.POST) public String updateUser(@Valid User user, BindingResult result, ModelMap model, @PathVariable String ssoId) { if (result.hasErrors()) { return "registration"; } /*//Uncomment below 'if block' if you WANT TO ALLOW UPDATING SSO_ID in UI which is a unique key to a User. if(!userService.isUserSSOUnique(user.getId(), user.getSsoId())){ FieldError ssoError =new FieldError("user","ssoId",messageSource.getMessage("non.unique.ssoId", new String[]{user.getSsoId()}, Locale.getDefault())); result.addError(ssoError); return "registration"; }*/ userService.updateUser(user); model.addAttribute("success", "User " + user.getFirstName() + " "+ user.getLastName() + " updated successfully"); return "registrationsuccess"; } /** * This method will delete an user by it's SSOID value. */ @RequestMapping(value = { "/delete-user-{ssoId}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET) public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String ssoId) { userService.deleteUserBySSO(ssoId); return "redirect:/list"; } /** * This method will provide UserProfile list to views */ @ModelAttribute("roles") public List<UserProfile> initializeProfiles() { return userProfileService.findAll(); } }
Сообщения, которые используются выше описаны в messages.properties файле:
NotEmpty.user.firstName=Поле имя не может быть пустым. NotEmpty.user.lastName=Поле фамилия не может быть пустым. NotEmpty.user.email=Поле маил не может быть пустым. NotEmpty.user.password=Поле пароля не может быть пустым. NotEmpty.user.ssoId=Поле SSO ID не может быть пустым. NotEmpty.user.userProfiles=Как минимум необходимо выбрать один профиль. non.unique.ssoId=SSO ID {0} уже существует. Пожалуйста, выберете другое значение.
Шаг 9: Создание конвертера
Это сердце это поста. Это заботится об отображение отдельных ID профилей пользователя к фактическим сущностям профилей пользователя в базе данных.
Класс RoleToUserProfileConverter
package com.websystique.springmvc.converter; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.UserProfile; import com.websystique.springmvc.service.UserProfileService; /** * A converter class used in views to map id's to actual userProfile objects. */ @Component public class RoleToUserProfileConverter implements Converter<Object, UserProfile>{ @Autowired UserProfileService userProfileService; /** * Gets UserProfile by Id * @see org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter#convert(java.lang.Object) */ public UserProfile convert(Object element) { Integer id = Integer.parseInt((String)element); UserProfile profile= userProfileService.findById(id); System.out.println("Profile : "+profile); return profile; } }
Шаг 10: Создание настроек Spring
Класс AppConfig
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.MessageSource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource; import org.springframework.format.FormatterRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.PathMatchConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewResolverRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView; import com.websystique.springmvc.converter.RoleToUserProfileConverter; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.websystique.springmvc") public class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{ @Autowired RoleToUserProfileConverter roleToUserProfileConverter; /** * Configure ViewResolvers to deliver preferred views. */ @Override public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) { InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class); viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/"); viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp"); registry.viewResolver(viewResolver); } /** * Configure ResourceHandlers to serve static resources like CSS/ Javascript etc... */ @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("/static/"); } /** * Configure Converter to be used. * In our example, we need a converter to convert string values[Roles] to UserProfiles in newUser.jsp */ @Override public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) { registry.addConverter(roleToUserProfileConverter); } /** * Configure MessageSource to lookup any validation/error message in internationalized property files */ @Bean public MessageSource messageSource() { ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); messageSource.setBasename("messages"); return messageSource; } /**Optional. It's only required when handling '.' in @PathVariables which otherwise ignore everything after last '.' in @PathVaidables argument. * It's a known bug in Spring [https://jira.spring.io/browse/SPR-6164], still present in Spring 4.1.7. * This is a workaround for this issue. */ @Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer matcher) { matcher.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(true); } } Во-первых интересной вещью является регистрационный конвертер, который мы создали в предыдущих уроках с настройкой Spring’a c использованием addFormatters. Следующий метод configurePathMatch, который обеспечивает обходной путь (хотя существуют и другие обходные пути) для известного бага в Spring, который также присутствует в Spring 4.1.7.RELEASE.
Установка конвертера в настройке XML, будет выглядеть следующим образом:
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"/> <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean"> <property name="converters"> <list> <bean id="roleToUserProfile" class="com.websystique.springsecurity.configuration.RoleToUserProfileConverter" /> </list> </property> </bean> Добавляем инициализирующий класс:
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; public class AppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class[] { AppConfig.class }; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return null; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[] { "/" }; } }
Шаг 11: Добавляем представления/JSP
Имейте ввиду, что мы используем Bootstrap для дизайна в JSP.
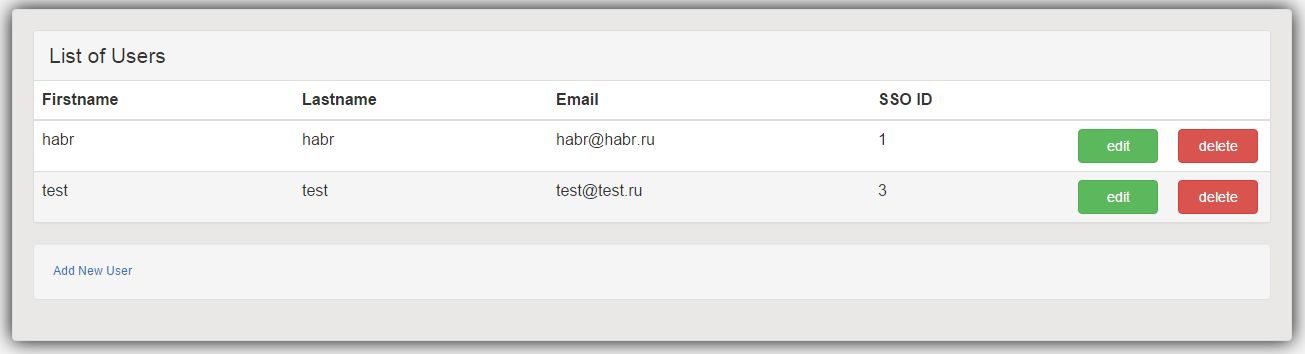
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Users List</title> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/bootstrap.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/app.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> </head> <body> <div class="generic-container"> <div class="panel panel-default"> <!-- Default panel contents --> <div class="panel-heading"><span class="lead">List of Users </span></div> <table class="table table-hover"> <thead> <tr> <th>Firstname</th> <th>Lastname</th> <th>Email</th> <th>SSO ID</th> <th width="100"></th> <th width="100"></th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <c:forEach items="${users}" var="user"> <tr> <td>${user.firstName}</td> <td>${user.lastName}</td> <td>${user.email}</td> <td>${user.ssoId}</td> <td><a href="<c:url value='/edit-user-${user.ssoId}' />" class="btn btn-success custom-width">edit</a></td> <td><a href="<c:url value='/delete-user-${user.ssoId}' />" class="btn btn-danger custom-width">delete</a></td> </tr> </c:forEach> </tbody> </table> </div> <div class="well"> <a href="<c:url value='/newuser' />">Add New User</a> </div> </div> </body> </html>
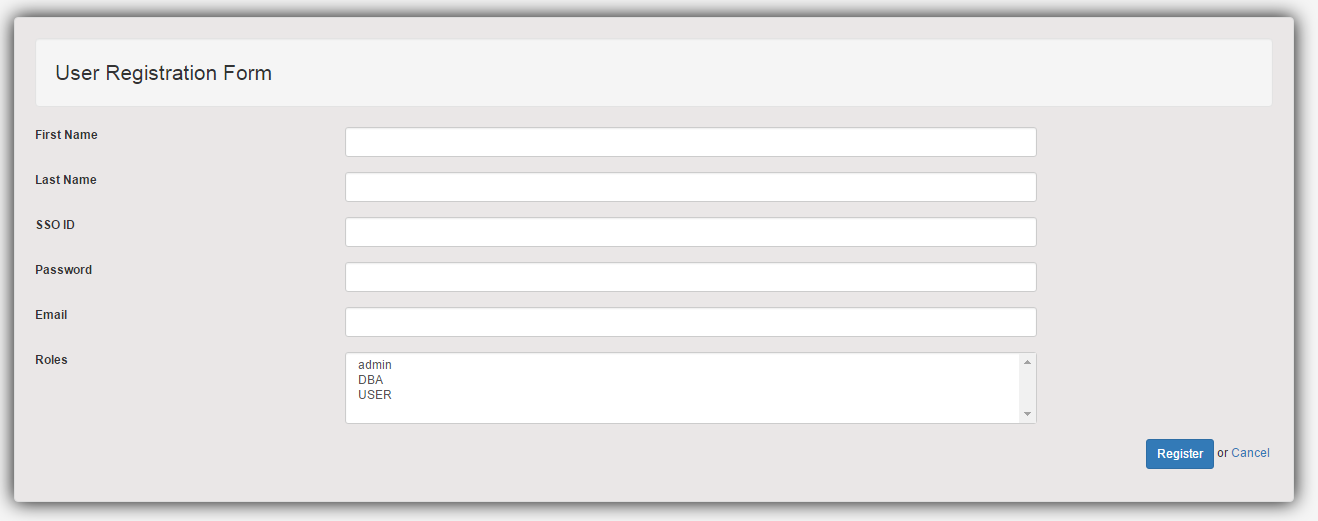
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>User Registration Form</title> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/bootstrap.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/app.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> </head> <body> <div class="generic-container"> <div class="well lead">User Registration Form</div> <form:form method="POST" modelAttribute="user" class="form-horizontal"> <form:input type="hidden" path="id" id="id"/> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="firstName">First Name</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <form:input type="text" path="firstName" id="firstName" class="form-control input-sm"/> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="firstName" class="help-inline"/> </div> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="lastName">Last Name</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <form:input type="text" path="lastName" id="lastName" class="form-control input-sm" /> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="lastName" class="help-inline"/> </div> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="ssoId">SSO ID</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <c:choose> <c:when test="${edit}"> <form:input type="text" path="ssoId" id="ssoId" class="form-control input-sm" disabled="true"/> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <form:input type="text" path="ssoId" id="ssoId" class="form-control input-sm" /> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="ssoId" class="help-inline"/> </div> </c:otherwise> </c:choose> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="password">Password</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <form:input type="password" path="password" id="password" class="form-control input-sm" /> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="password" class="help-inline"/> </div> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="email">Email</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <form:input type="text" path="email" id="email" class="form-control input-sm" /> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="email" class="help-inline"/> </div> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-group col-md-12"> <label class="col-md-3 control-lable" for="userProfiles">Roles</label> <div class="col-md-7"> <form:select path="userProfiles" items="${roles}" multiple="true" itemValue="id" itemLabel="type" class="form-control input-sm" /> <div class="has-error"> <form:errors path="userProfiles" class="help-inline"/> </div> </div> </div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="form-actions floatRight"> <c:choose> <c:when test="${edit}"> <input type="submit" value="Update" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm"/> or <a href="<c:url value='/list' />">Cancel</a> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <input type="submit" value="Register" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm"/> or <a href="<c:url value='/list' />">Cancel</a> </c:otherwise> </c:choose> </div> </div> </form:form> </div> </body> </html>
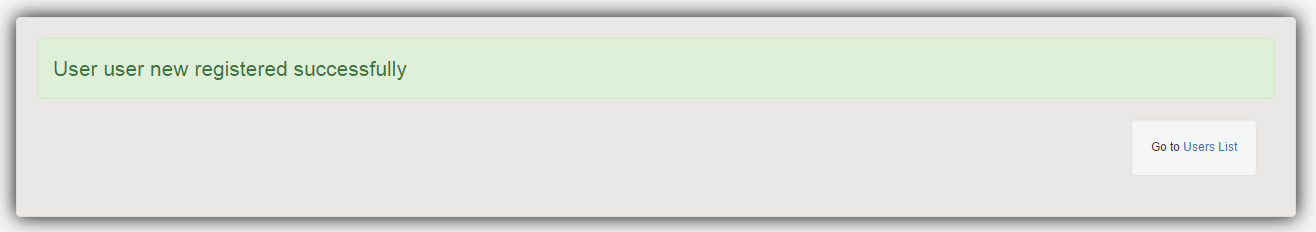
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Registration Confirmation Page</title> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/bootstrap.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> <link href="<c:url value='/static/css/app.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link> </head> <body> <div class="generic-container"> <div class="alert alert-success lead"> ${success} </div> <span class="well floatRight"> Go to <a href="<c:url value='/list' />">Users List</a> </span> </div> </body> </html>
И крошечный файл стилей:
app.css
body, #mainWrapper { height: 100%; background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245); } body, .form-control{ font-size:12px!important; } .floatRight{ float:right; margin-right: 18px; } .has-error{ color:red; } .generic-container { position:fixed; width:80%; margin-left: 20px; margin-top: 20px; margin-bottom: 20px; padding: 20px; background-color: #EAE7E7; border: 1px solid #ddd; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 0 30px black; } .custom-width { width: 80px !important; }
Шаг 12: Создать, развертывать и запуск приложения
Сейчас мы можем сразу через IDE запустить проект или же экспортировать его в .war файл.
Скриншоты приложения:


Заключение
Мы создали приложение Spring MVC используя отношения многие-ко-многим и аннотации Hibernate.
ссылка на оригинал статьи http://habrahabr.ru/post/271025/
Добавить комментарий