В этой статье будет рассматриваться проект nginx-log-collector, который будет читать логи nginx, отправлять их в кластер Clickhouse. Обычно для логов используют ElasticSearch. Для Clickhouse требуется меньше ресурсов (дисковое пространство, ОЗУ, ЦПУ). Clickhouse быстрее записывает данные. Clickhouse сжимает данные, что делает данные на диске еще компактнее. Преимущества Clickhouse видны по 2 слайдам с доклада Как VK вставляет данные в ClickHouse с десятков тысяч серверов.


Для просмотра аналитики по логам создадим дашборд для Grafana.
Кому интересно, добро пожаловать под кат.
Устанавливаем nginx, grafana стандартным способом.
Устанавливаем кластер clickhouse с помощью ansible-playbook от Дениса Проскурина.
Создание бд и таблиц в Clickhouse
В этом файле описаны SQL запросы для создания бд и таблиц для nginx-log-collector в Clickhouse.
Каждый запрос делаем поочередно на каждом сервере кластера Clickhouse.
Важное замечание. В этой строке logs_cluster нужно заменить на ваше название кластера из файла clickhouse_remote_servers.xml между "remote_servers" and "shard".
ENGINE = Distributed('logs_cluster', 'nginx', 'access_log_shard', rand())
Устанавливка и настройка nginx-log-collector-rpm
Nginx-log-collector не имеет rpm. Здесь https://github.com/patsevanton/nginx-log-collector-rpm создаем ему rpm. Собираться rpm будет с помощью Fedora Copr
Устанавливаем rpm пакет nginx-log-collector-rpm
yum -y install yum-plugin-copr yum copr enable antonpatsev/nginx-log-collector-rpm yum -y install nginx-log-collector systemctl start nginx-log-collector
Правим конфиг /etc/nginx-log-collector/config.yaml:
....... upload: table: nginx.access_log dsn: http://ip-адрес-кластера-clickhouse:8123/ - tag: "nginx_error:" format: error # access | error buffer_size: 1048576 upload: table: nginx.error_log dsn: http://ip-адрес-кластера-clickhouse:8123/
Настройка nginx
Общий конфиг nginx:
user nginx; worker_processes auto; #error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; log_format avito_json escape=json '{' '"event_datetime": "$time_iso8601", ' '"server_name": "$server_name", ' '"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", ' '"remote_user": "$remote_user", ' '"http_x_real_ip": "$http_x_real_ip", ' '"status": "$status", ' '"scheme": "$scheme", ' '"request_method": "$request_method", ' '"request_uri": "$request_uri", ' '"server_protocol": "$server_protocol", ' '"body_bytes_sent": $body_bytes_sent, ' '"http_referer": "$http_referer", ' '"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent", ' '"request_bytes": "$request_length", ' '"request_time": "$request_time", ' '"upstream_addr": "$upstream_addr", ' '"upstream_response_time": "$upstream_response_time", ' '"hostname": "$hostname", ' '"host": "$host"' '}'; access_log syslog:server=unix:/var/run/nginx_log.sock,nohostname,tag=nginx avito_json; #ClickHouse error_log syslog:server=unix:/var/run/nginx_log.sock,nohostname,tag=nginx_error; #ClickHouse #access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; proxy_ignore_client_abort on; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; }
Виртуальный хост один:
vhost1.conf:
upstream backend { server ip-адрес-сервера-с-stub_http_server:8080; server ip-адрес-сервера-с-stub_http_server:8080; server ip-адрес-сервера-с-stub_http_server:8080; server ip-адрес-сервера-с-stub_http_server:8080; server ip-адрес-сервера-с-stub_http_server:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name vhost1; location / { proxy_pass http://backend; } }
Добавляем в файл /etc/hosts виртуальные хосты:
ip-адрес-сервера-с-nginx vhost1
Эмулятор HTTP сервера
В качестве эмулятора HTTP сервера будем использовать nodejs-stub-server от Maxim Ignatenko
Nodejs-stub-server не имеет rpm. Здесь https://github.com/patsevanton/nodejs-stub-server создаем ему rpm. Собираться rpm будет с помощью Fedora Copr
Устанавливаем на upstream nginx rpm пакет nodejs-stub-server
yum -y install yum-plugin-copr yum copr enable antonpatsev/nodejs-stub-server yum -y install stub_http_server systemctl start stub_http_server
Нагрузочное тестирование
Тестирование проводим с помощью Apache benchmark.
Устанавливаем его:
yum install -y httpd-tools
Запускаем тестирование с помощью Apache benchmark c 5 разных серверов:
while true; do ab -H "User-Agent: 1server" -c 10 -n 10 -t 10 http://vhost1/; sleep 1; done while true; do ab -H "User-Agent: 2server" -c 10 -n 10 -t 10 http://vhost1/; sleep 1; done while true; do ab -H "User-Agent: 3server" -c 10 -n 10 -t 10 http://vhost1/; sleep 1; done while true; do ab -H "User-Agent: 4server" -c 10 -n 10 -t 10 http://vhost1/; sleep 1; done while true; do ab -H "User-Agent: 5server" -c 10 -n 10 -t 10 http://vhost1/; sleep 1; done
Настройка Grafana
На официальном сайте Grafana вы не найдете дашборд.
Поэтому будем делать его вручую.
Мой сохраненный дашборд вы можете найти тут.
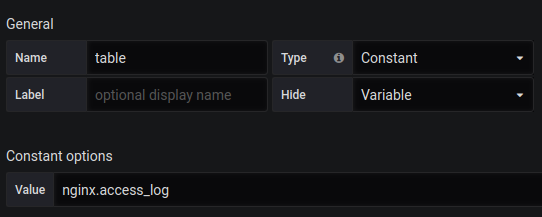
Так же вам нужно создать переменную table с содержимым nginx.access_log.
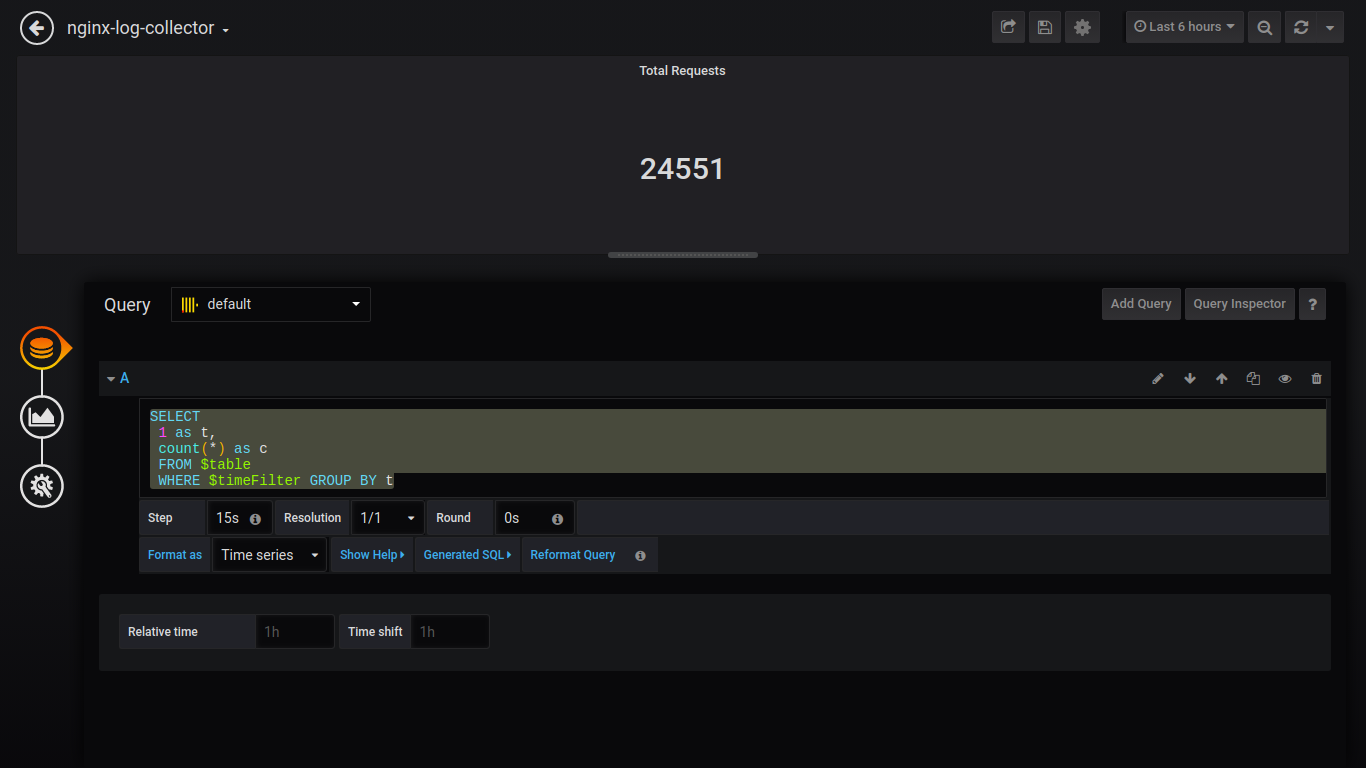
Singlestat Total Requests:
SELECT 1 as t, count(*) as c FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY t
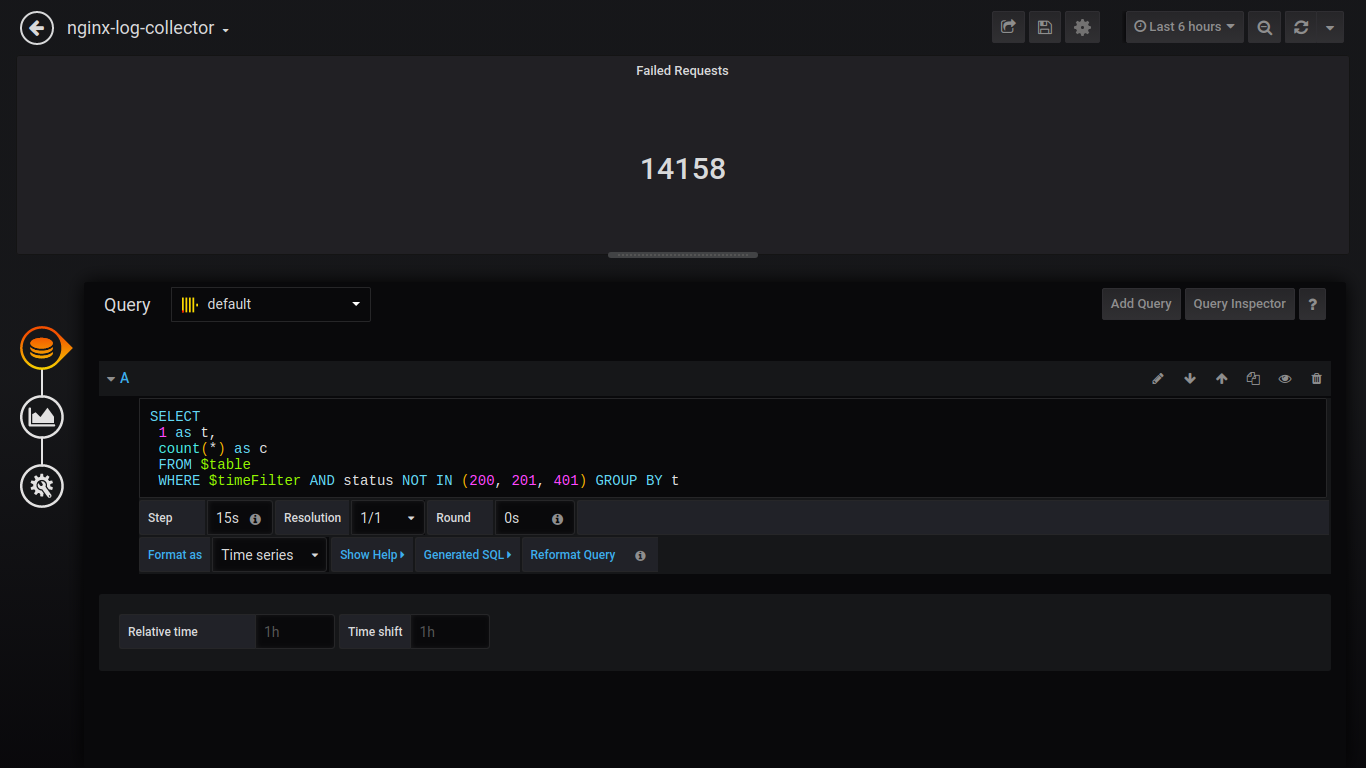
Singlestat Failed Requests:
SELECT 1 as t, count(*) as c FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter AND status NOT IN (200, 201, 401) GROUP BY t
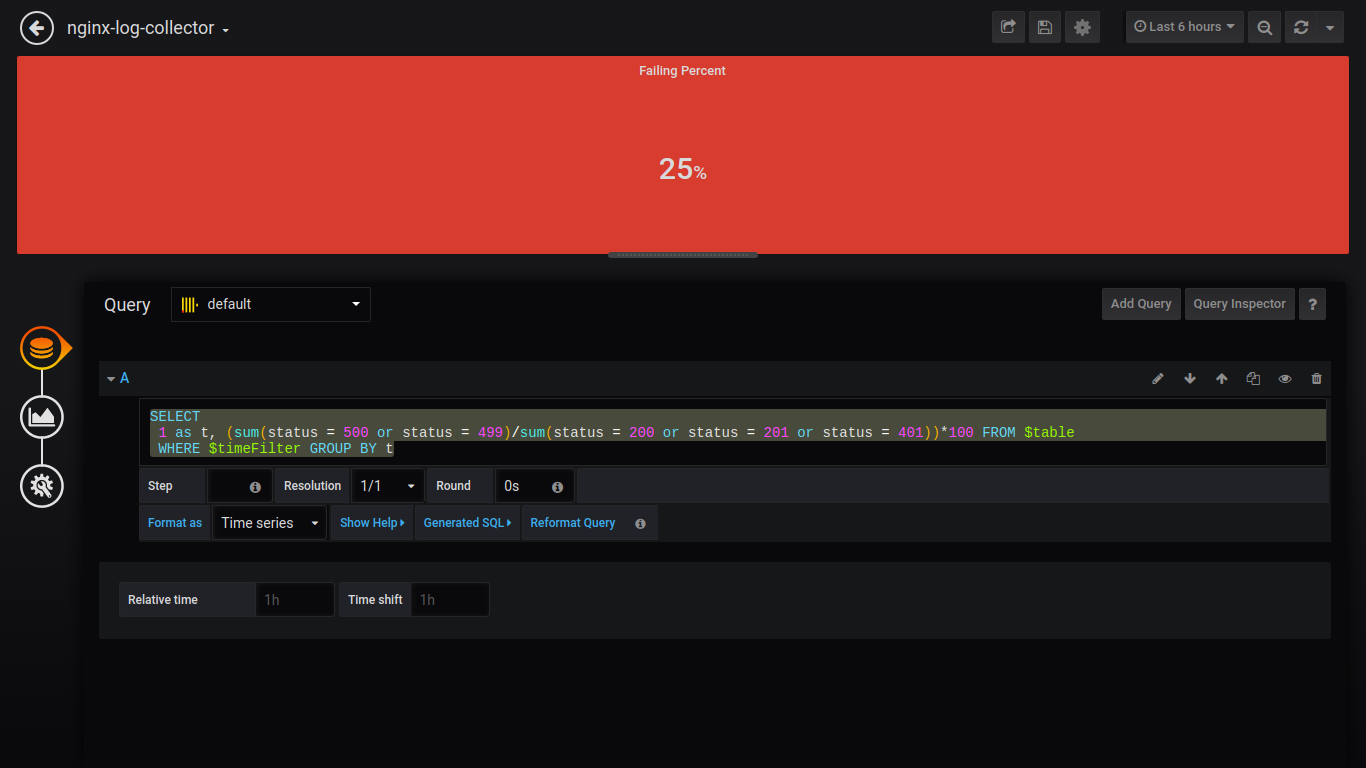
Singlestat Failing Percent:
SELECT 1 as t, (sum(status = 500 or status = 499)/sum(status = 200 or status = 201 or status = 401))*100 FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY t
Singlestat Avg Response Time:
SELECT 1, avg(request_time) FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY 1
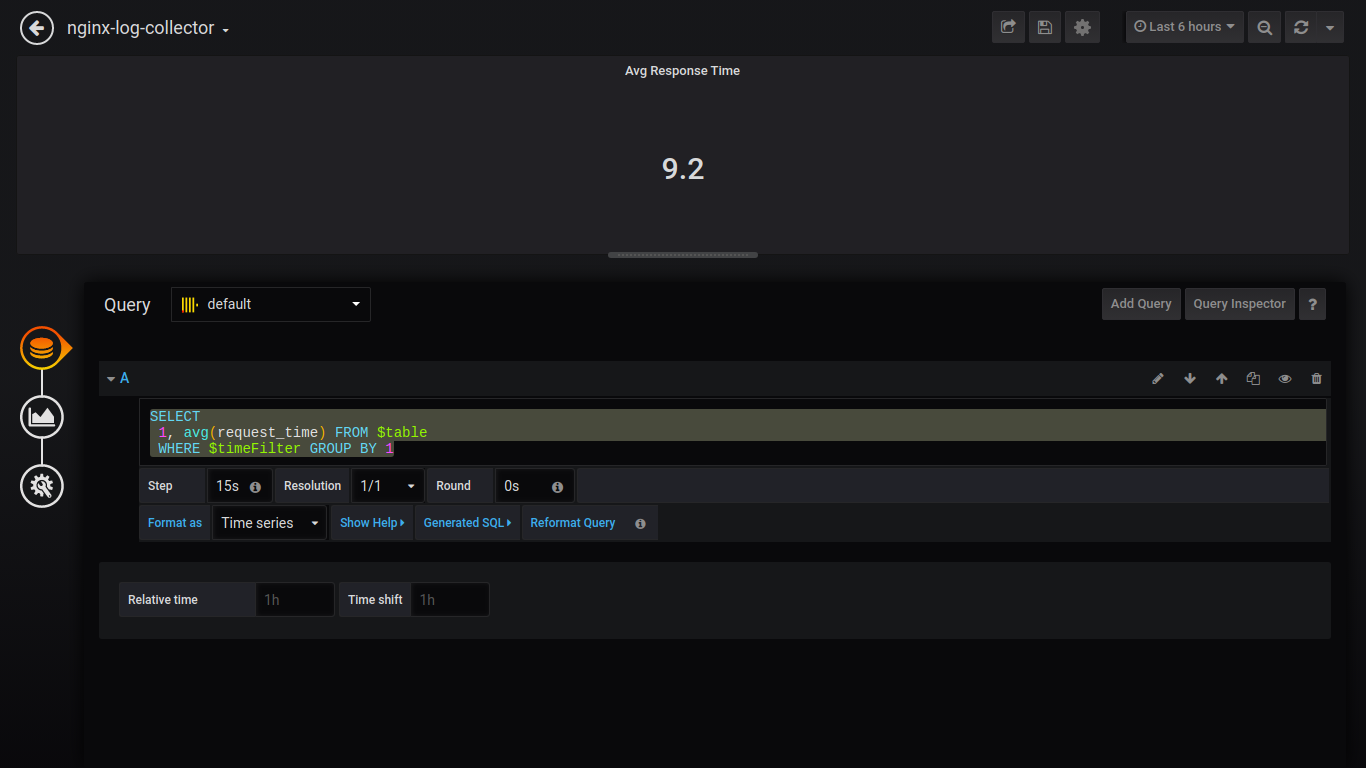
Singlestat Max Response Time:
SELECT 1 as t, max(request_time) as c FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY t
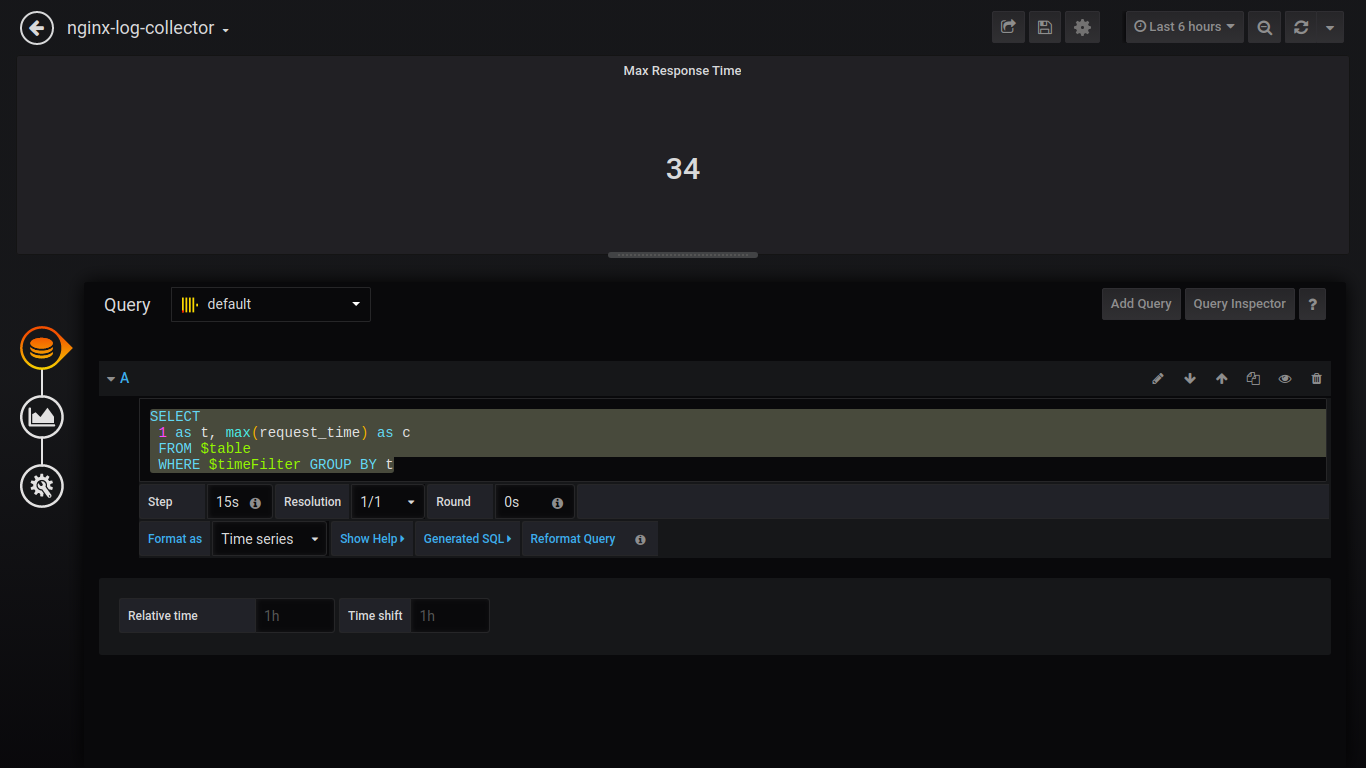
Count Status:
$columns(status, count(*) as c) from $table
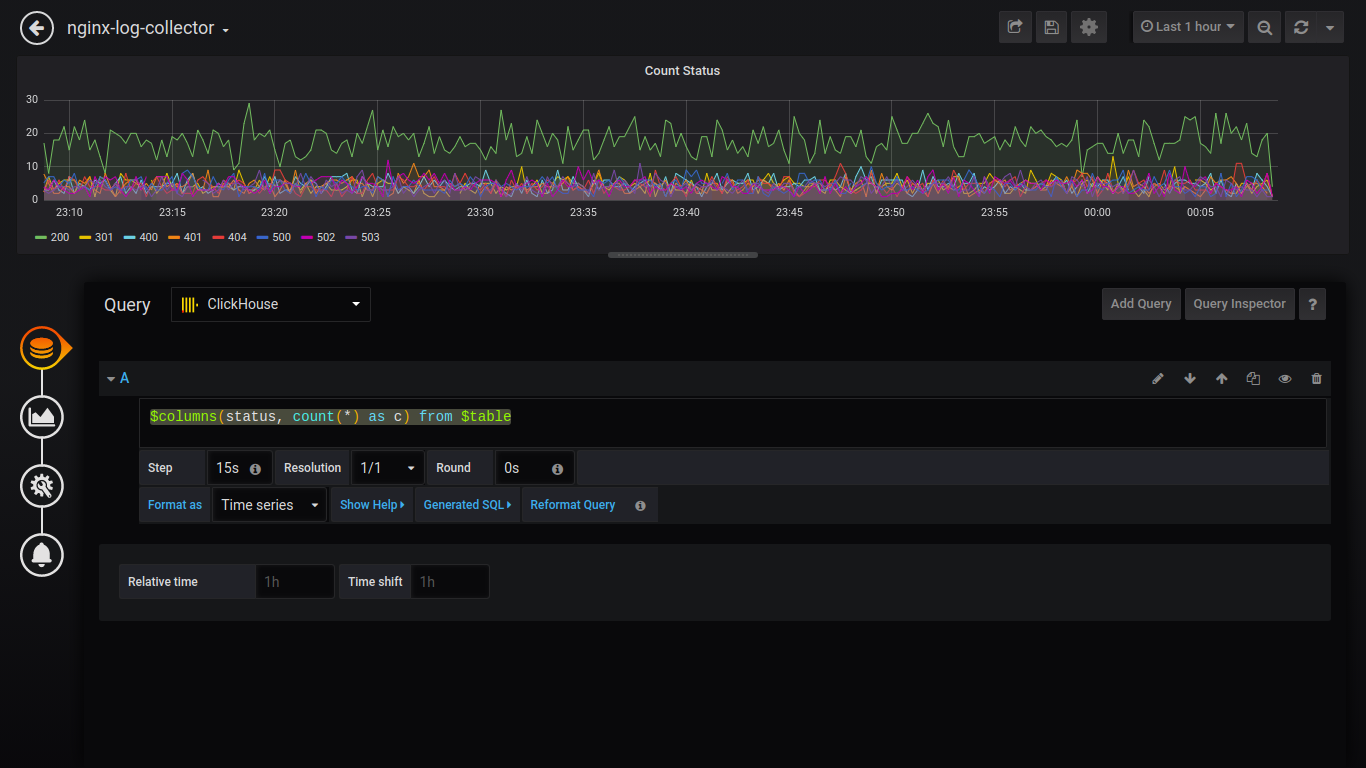
Для вывода данных как пирог, нужно установить плагин и перезагрузить grafana.
grafana-cli plugins install grafana-piechart-panel service grafana-server restart
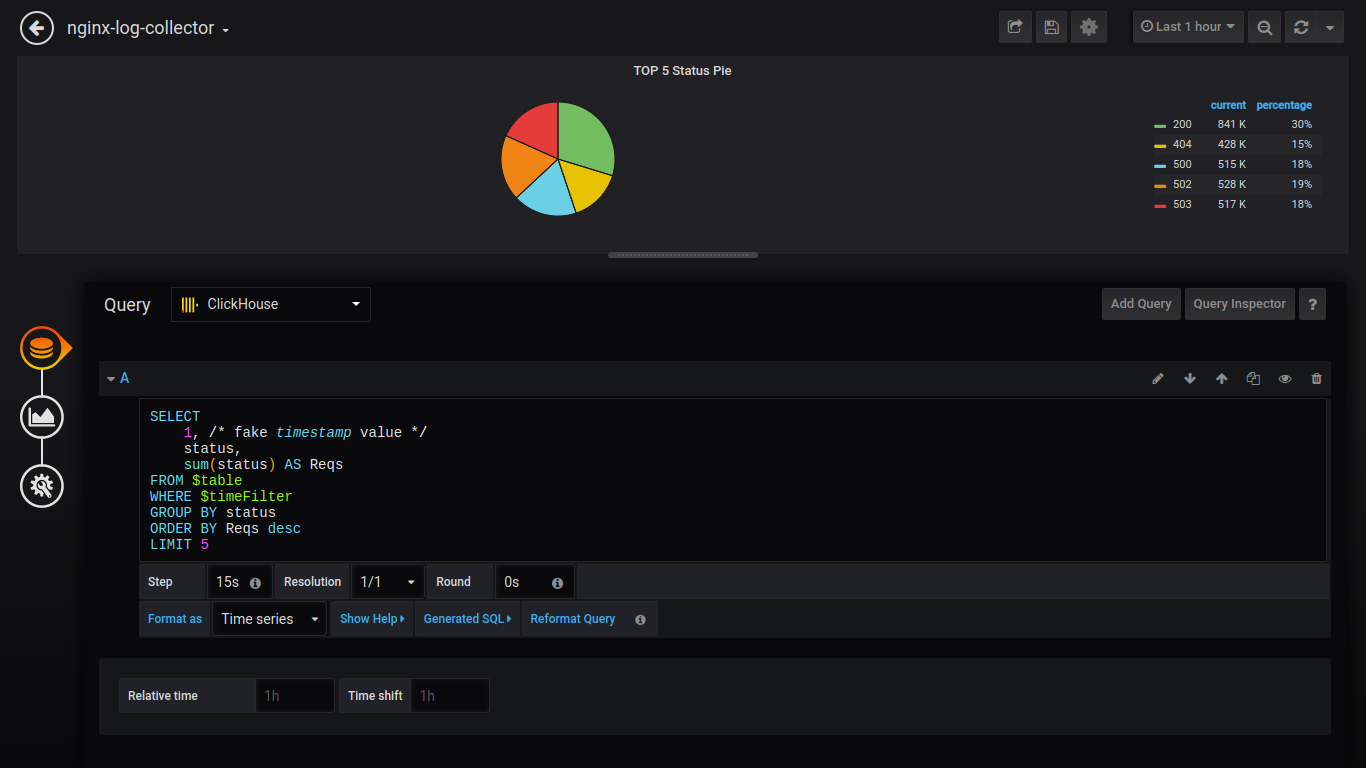
Pie TOP 5 Status:
SELECT 1, /* fake timestamp value */ status, sum(status) AS Reqs FROM $table WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY status ORDER BY Reqs desc LIMIT 5
Дальше буду приводить запросы без скриншотов:
Count http_user_agent:
$columns(http_user_agent, count(*) c) FROM $table
GoodRate/BadRate:
$rate(countIf(status = 200) AS good, countIf(status != 200) AS bad) FROM $table
Response Timing:
$rate(avg(request_time) as request_time) FROM $table
Upstream response time (время ответа 1-го upstream):
$rate(avg(arrayElement(upstream_response_time,1)) as upstream_response_time) FROM $table
Table Count Status for all vhost:
$columns(status, count(*) as c) from $table
Общий вид дашборда
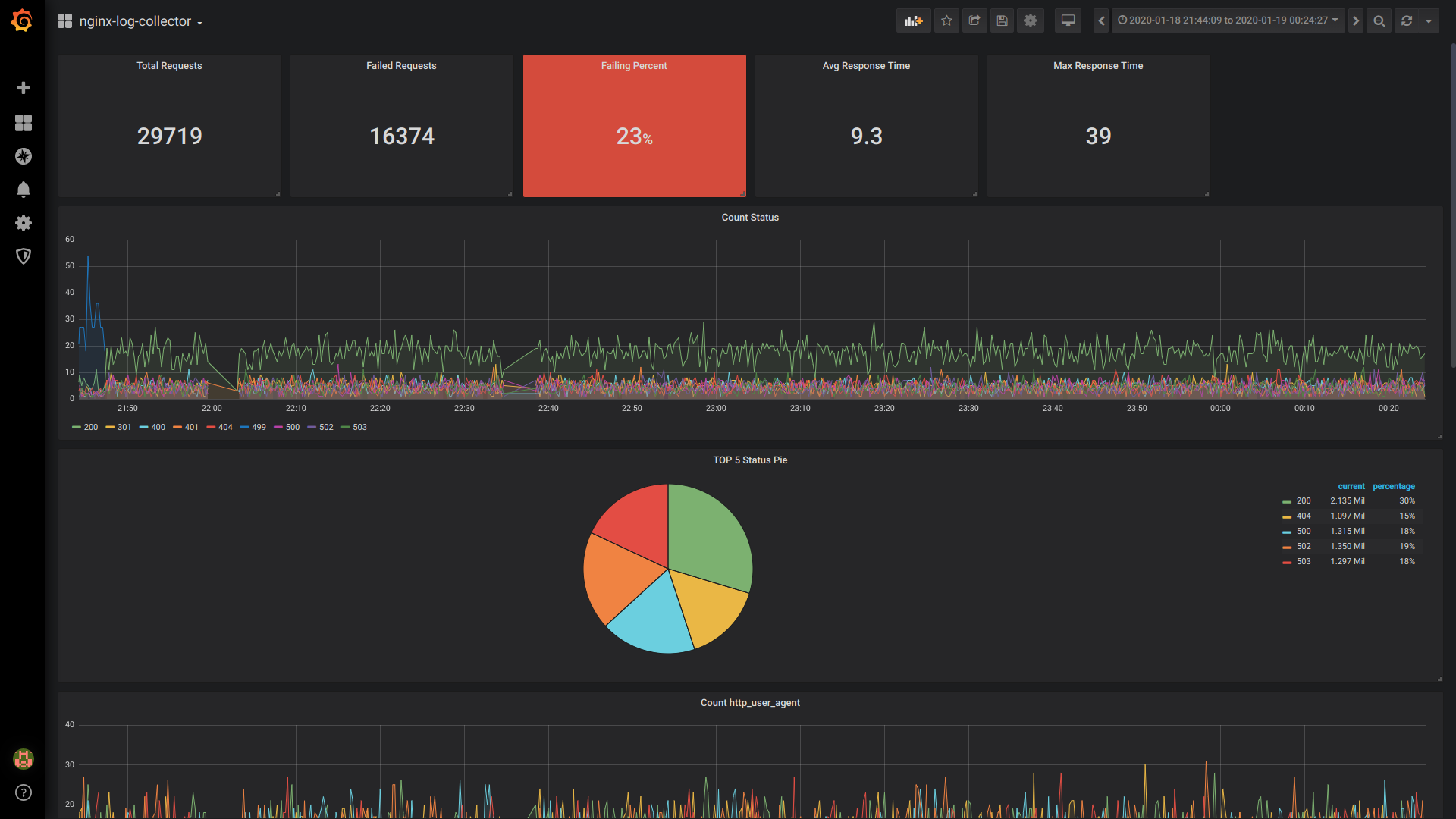

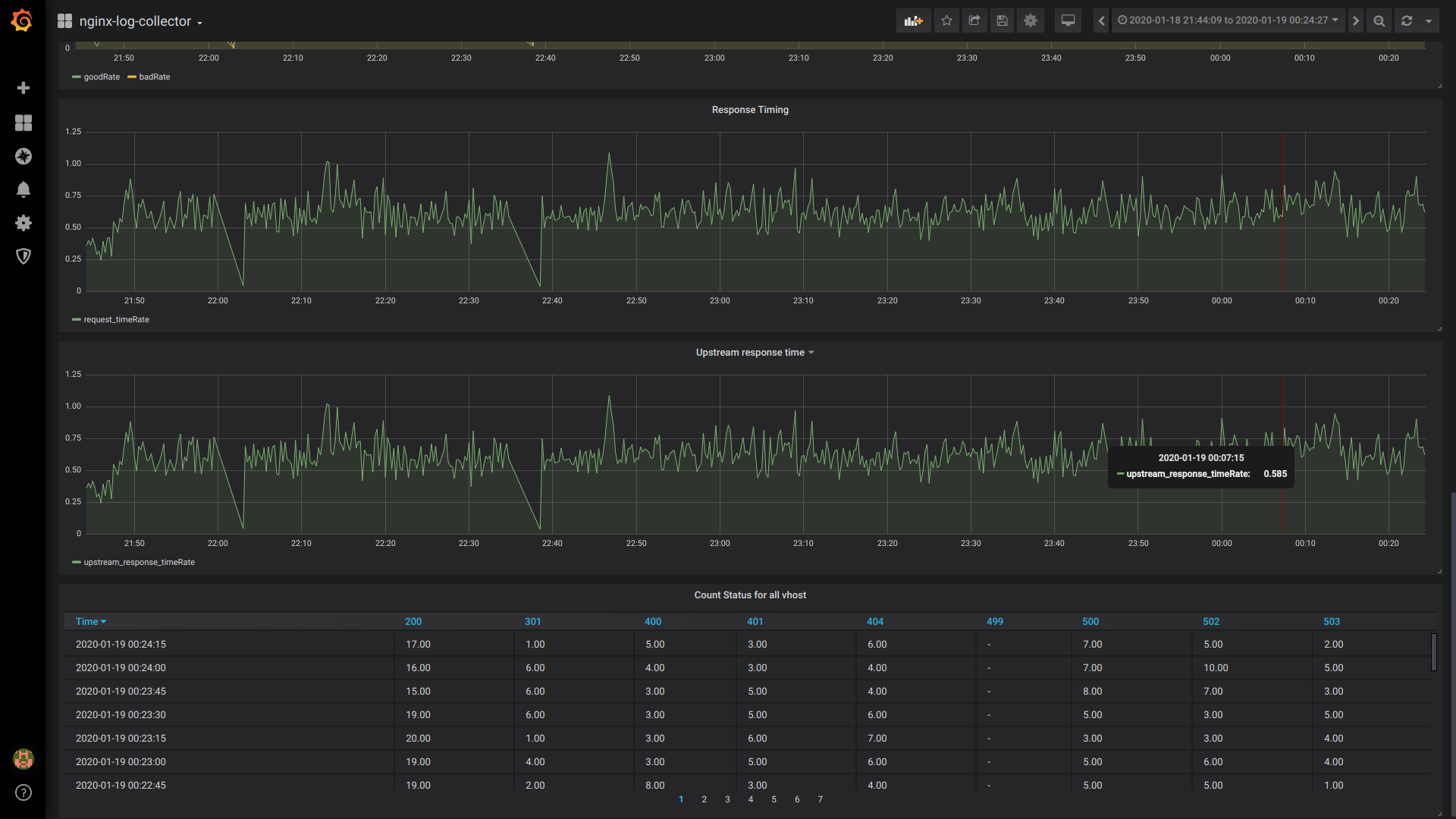
Вывод:
Надеюсь, сообщество подключится к разработке/тестированию и использованию nginx-log-collector.
И кто-нибудь когда внедрит nginx-log-collector расскажет сколько сэкономил диска, ОЗУ, ЦПУ.
Telegram каналы:
Миллисекунды:
Кому важны миллисекунды, напишите или проголосуйте, пожалуйста, в этом issue.
ссылка на оригинал статьи https://habr.com/ru/post/484640/
Добавить комментарий