Обзор
Здравствуйте! В этой статье я хочу описать программу валидации XML с помощью Spring Framework. Наиболее очевидная область применения такой валидации — это программирование web-сервисов.
Валидация производится через преобразование XML-Java (unmarshalling) по соответствующей XSD-схеме. XML-файл считается прошедшим проверку, если преобразование XML в объект Java прошло успешно.
Проект компилируется в jar файл и запускается в командной строке. Для красоты прикручен Apache ANSI Printer, в котором можно задавать шрифт, цвет и выделение текста в cmd.
Исходный код доступен в GitHub по ссылке XmlProcessor.
Итак, приступим.
1. Исходные файлы и схемы
В качестве входных данных определим 2 XML файла Address.xml и Client.xml.
Address.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ns:Request xmlns:ns="http://www.tempuri.org/types"> <Version>V001.000.00</Version> <Address> <Apartment>50</Apartment> <House>7</House> <Street>Sadovaya</Street> <City>SPB</City> <Country>Russia</Country> <Index>123456</Index> </Address> </ns:Request>
Client.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ns:Request xmlns:ns="http://www.tempuri.org/types"> <Version>V001.000.00</Version> <Client> <Id>12</Id> <Name>A</Name> </Client> <Client> <Id>34</Id> <Name>B</Name> </Client> </ns:Request>
Далее определим XSD-схемы XmlValidator.xsd, ComplexTypes.xsd и SimpleTypes.xsd с
описанием контейнера CombinedType и объектов типа Address и Client:
XmlValidator.xsd:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:ns="http://www.tempuri.org/types" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:ict="complextypes" targetNamespace="http://www.tempuri.org/types" elementFormDefault="qualified"> <xsd:import namespace="complextypes" schemaLocation="complextypes.xsd"/> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>XSD structure</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:element name="Combined" type="ict:CombinedType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>XML definition</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="complextypes" xmlns:ist="simpletypes" targetNamespace="complextypes"> <xsd:import namespace="simpletypes" schemaLocation="simpletypes.xsd"/> <xsd:complexType name="CombinedType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="Version" type="ist:VersionType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The version</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:choice> <xsd:element name="Address" type="AddressType" maxOccurs="1"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Address type</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="Client" type="ClientType" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Client type</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:choice> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="AddressType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="Apartment" type="ist:ApartmentType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Apartment number</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="House" type="ist:HouseNumberType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>House number</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="Street" type="ist:StreetType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Street name</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="City" type="ist:CityType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>City name</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="Country" type="ist:CountryType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Country name</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="Index" type="ist:IndexType" minOccurs="0"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Postal index</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:complexType name="ClientType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="Id" type="ist:IdType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The id</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="Name" type="ist:NameType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The name</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="simpletypes" targetNamespace="simpletypes"> <xsd:simpleType name="VersionType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>V000.000.00</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:maxLength value="11"/> <xsd:pattern value="V[0-9]{3}.[0-9]{3}.[0-9]{2}"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="IdType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Int, 10 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:nonNegativeInteger"> <xsd:totalDigits value="10"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="NameType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>String, 50 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:maxLength value="50"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="ApartmentType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Int, 4 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:nonNegativeInteger"> <xsd:totalDigits value="4"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="HouseNumberType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Int, 3 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:nonNegativeInteger"> <xsd:totalDigits value="3"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="StreetType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>String, 40 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:maxLength value="40"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="CityType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>City, 40 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:maxLength value="40"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="CountryType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Country, 30 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"> <xsd:maxLength value="30"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType name="IndexType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Int, 10 max</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> <xsd:restriction base="xsd:nonNegativeInteger"> <xsd:totalDigits value="10"/> </xsd:restriction> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
Обратите внимание на элемент <xsd:choice> в CombinedType схемы ComplexTypes.xsd. Он означает, что xml-файл должен содержать либо один элемент типа Address, либо один или несколько элементов типа Client.
2. Конфигурация Spring
В файле spring-config.xml находится описание используемых в проекте бинов Printer,
FileReader, Marshaller, XMLService. Помимо указанных бинов, определен фильтр расширений
FileNameExtensionFilter, чтобы рассматривать только xml-файлы.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-2.0.xsd"> <!-- Printer --> <bean id="printer" class="com.xmlprocessor.service.impl.AnsiConsolePrinter"/> <!-- FilenameExtensionFilter --> <bean id="filenameExtensionFilter"class= "com.xmlprocessor.util.FilenameExtensionFilter"> <constructor-arg index="0"> <list> <value>xml</value> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- FileReader --> <bean id="fileReader" class="com.xmlprocessor.service.impl.FileReader"> <property name="filenameFilter" ref="filenameExtensionFilter" /> </bean> <!-- Marshaller --> <bean id="marshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller"> <property name="classesToBeBound"> <list> <value>com.xmlprocessor.types.CombinedType</value> </list> </property> <property name="schemas"> <list> <value>xmlvalidator.xsd</value> <value>complextypes.xsd</value> <value>simpletypes.xsd</value> </list> </property> <property name="marshallerProperties"> <map> <entry> <key> <util:constant static-field= "javax.xml.bind.Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT"/> </key> <value type="java.lang.Boolean">true</value> </entry> </map> </property> </bean> <!-- XmlService --> <bean id="xmlService" class="com.xmlprocessor.service.impl.XmlService"> <property name="printer" ref="printer" /> <property name="marshaller" ref="marshaller" /> <property name="unmarshaller" ref="marshaller" /> </bean> </beans>
3. Преобразование XML-Java
В точке входа приложения XmlProcessorDrv сначала считываем и проверяем аргументы
командной строки, затем через вызов методов класса Compositor создаем бины printer,
fileReader и xmlService. Далее считываем xml-файлы и выполняем валидацию файлов в
директории, указанной в CLI_OPTION_DIRECTORY.
Самое интересное происходит при вызове
xmlService.validate(xmlFiles)
package com.xmlprocessor.main; import java.io.File; import java.util.List; import com.xmlprocessor.config.Compositor; import com.xmlprocessor.service.api.PrinterInt; import com.xmlprocessor.service.api.XmlServiceInt; import com.xmlprocessor.util.CommandLineArgs; public class XmlProcessorDrv { /** Name of the program */ private static final String PROG_NAME = XmlProcessorDrv.class.getSimpleName(); /** Version of the Program */ private static final String PROG_VERSION = "1.0 (XmlProcessor v1.000)"; /** Exit Status {@value} for OK. */ private static final int EXIT_STATUS_OK = 0; /** Exit Status {@value} for not OK. */ private static final int EXIT_STATUS_NOT_OK = -1; /** * Main entry point. * Evaluates command line args and validates provided xml files * * @param args * Command line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { // execution status int exitStatus; // get printer object PrinterInt printer = Compositor.getPrinter(); // read command line args CommandLineArgs cmdLineArgs = new CommandLineArgs(args); // Show version if (cmdLineArgs.hasOption(CommandLineArgs.CLI_OPTION_VERSION)) { printer.printf("%s v%s\n", PROG_NAME, PROG_VERSION); } // Show help if (cmdLineArgs.hasOption(CommandLineArgs.CLI_OPTION_HELP)) { cmdLineArgs.printHelp(PROG_NAME); } // Check if the directory name is passed in args if (!cmdLineArgs.hasOption(CommandLineArgs.CLI_OPTION_DIRECTORY)) { cmdLineArgs.printHelp(PROG_NAME); return; } String dir = cmdLineArgs.getOptionValue(CommandLineArgs.CLI_OPTION_DIRECTORY); printer.printf("\n%s %s","Folder with XML files: ", dir); List<File> xmlFiles; XmlServiceInt xmlService = Compositor.getXmlService(); try { xmlFiles = Compositor.getFileReader().readFiles(dir); printer.bold("\n\nStart validating XML files:\n"); xmlService.validate(xmlFiles); exitStatus = EXIT_STATUS_OK; } catch (Exception ex) { printer.errorln("\n" + ex.getMessage()); exitStatus = EXIT_STATUS_NOT_OK; } System.exit(exitStatus); } // main }
Код метода validate представлен ниже.
... /** {@inheritDoc} */ public void validate(List<File> xmlFiles) throws Exception { int fileCount = xmlFiles.size(); File currentFile; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; Source xmlFileSource; CombinedType combinedType; AddressType addressType; for (int count = 0; count < fileCount; count++) { currentFile = xmlFiles.get(count); printer.boldln("Current file: ").println(currentFile.getPath()); try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(currentFile); xmlSource = new StreamSource(fileInputStream); combinedType = (CombinedType)unmarshaller.unmarshal(xmlSource); printer.boldln("Xml file [" + currentFile.getName() + "] validation success!\n"); printer.boldln("Version: ").println(combinedType.getVersion()); addressType = combinedType.getAddress(); if (addressType != null) { printer.boldln("Address: ").println(addressType.toString()); } else if (combinedType.getClients() != null) { int i=0; for (ClientType client : combinedType.getClients()) { printer.boldln("Client").println("[" + ++i + "]" + client.toString()); } } } catch(Exception e) { printer.fatalln("Xml file [" + currentFile.getName() + "] validation error: \n" + e.getMessage()); } finally { if (fileInputStream != null) { fileInputStream.close(); } } } printer.boldln("Validating complete."); }
Ключевое преобразование XML-Java или unmarshalling происходит в строке
combinedType = (CombinedType)unmarshaller.unmarshal(xmlSource);
Как уже упоминалось, если удалось из XML получить java-объект типа CombinedType, то
XML признается корректным.
Unmarshaller-у должен быть заранее известен конечный объект преобразования. Для
этого с помощью JAXB создадим файлы AddressType.java, ClientType.java, CombinedType.java
В IDE Eclipse: правый клик по XSD -> Generate -> JAXB Classes…

В итоге:
package com.xmlprocessor.types; import java.math.BigInteger; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType; /** * <p>Java class for AddressType complex type.</p> */ @SuppressWarnings("restriction") @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) @XmlType(name = "AddressType", propOrder = { "apartment", "street", "house", "city", "country", "index" }) public class AddressType { @XmlElement(name = "Apartment", required = true) protected Integer apartment; @XmlElement(name = "House", required = true) protected BigInteger house; @XmlElement(name = "Street", required = true) protected String street; @XmlElement(name = "City", required = true) protected String city; @XmlElement(name = "Country", required = true) protected String country; @XmlElement(name = "Index") protected BigInteger index; public Integer getApartment() { return apartment; } public void setApartment(Integer value) { this.apartment = value; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String value) { this.street = value; } public BigInteger getHouse() { return house; } public void setHouse(BigInteger value) { this.house = value; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String value) { this.city = value; } public String getCountry() { return country; } public void setCountry(String value) { this.country = value; } public BigInteger getIndex() { return index; } public void setIndex(BigInteger value) { this.index = value; } public boolean isSetIndex() { return (this.index!= null); } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("\nApartment#: " + apartment); sb.append("\nHouse#: " + house); sb.append("\nStreet: " + street); sb.append("\nCity: " + city); sb.append("\nCountry: " + country); if (this.isSetIndex()) { sb.append("\nIndex: " + index); } return sb.toString(); } }
package com.xmlprocessor.types; import java.math.BigInteger; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType; @SuppressWarnings("restriction") @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) @XmlType(name = "ClientType", namespace = "http://www.tempuri.org/complextypes", propOrder = { "id", "name" }) public class ClientType { @XmlElement(name = "Id", required = true) protected BigInteger id; @XmlElement(name = "Name", required = true) protected String name; public BigInteger getId() { return id; } public void setId(BigInteger value) { this.id = value; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String value) { this.name = value; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("\nId: " + id); sb.append("\nName: " + name); return sb.toString(); } }
package com.xmlprocessor.types; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType; /** * <p>Java class for CombinedType complex type. */ @SuppressWarnings("restriction") @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD) @XmlType(name = "CombinedType", propOrder = { "version", "clients", "address" }) @XmlRootElement(name = "Combined", namespace = "http://www.tempuri.org/types") public class CombinedType { @XmlElement(name = "Version", required = true) protected String version; @XmlElement(name = "Client") protected List<ClientType> clients; @XmlElement(name = "Address") protected AddressType address; public String getVersion() { return version; } public void setVersion(String value) { this.version = value; } public List<ClientType> getClients() { if (clients == null) { clients = new ArrayList<ClientType>(); } return this.clients; } public AddressType getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(AddressType value) { this.address = value; } }
4. Демонстрация работы программы
В проект включен файл Readme с описанием доступных опций и аргументов командной
строки:
XmlProcessor v1.0 Usage: java -jar XmlProcessorDrv [-d <Dir>] [-h] [-v] -h,--help Display this help -v Version of the program -d <Dir> Folder with XML files to be validated Example: java -jar xmlProcessor.jar --help -v -d "C:\\XmlSample"
Для запуска проекта из cmd скомпилируем jar, вызвав Maven build package на pom.xml, и в
cmd введем вышеописанную команду
java -jar xmlProcessor.jar -h -v -d «C:\XmlSample»
Директория C:\XmlSample должна содержать один или несколько файлов вида Address.xml и
Client.xml. Файлы с расширением не xml будут проигнорированы.
Пример корректной работы программы:

Программа выдаст ошибку, если длина поля превышает установленный в SimpleTypes.xsd предел, имеется опечатка в имени узла, итд. Для примера допустим, что первый элемент адреса написан как AApartment:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ns:Combined xmlns:ns="http://www.tempuri.org/types"> <Version>V001.000.00</Version> <Address> <AApartment>50</Apartment> <House>7</House> <Street>Sadovaya</Street> <City>Saint Petersburg</City> <Country>Russia</Country> <Index>123456</Index> </Address> </ns:Combined>
В этом случае программа выдаст ошибку:
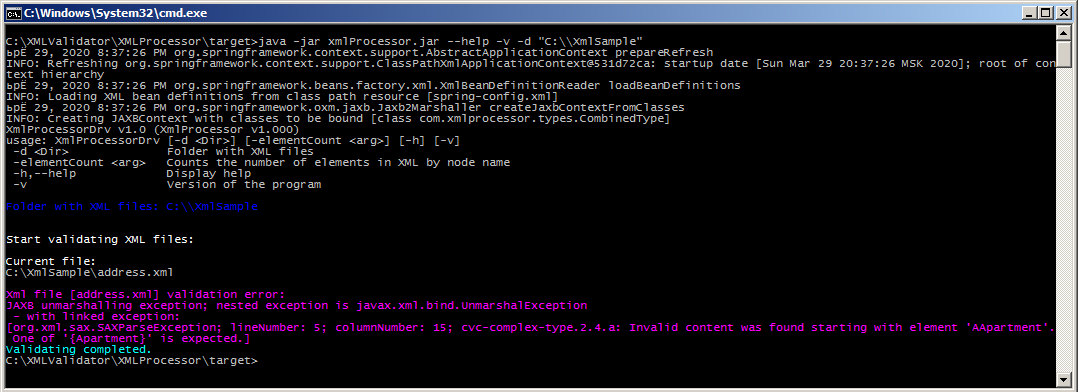
Спасибо за внимание.
ссылка на оригинал статьи https://habr.com/ru/post/495282/
Добавить комментарий