Шаг 1 — описать конечные положения
Тег для нашего виртуального вьюпорта будет называться custom-viewport. Итак, сперва опишем общие свойства для вьюпорта:
custom-viewport { min-height: 50vh; max-height: 100vh; width: 100%; position: absolute; bottom: 0; overflow: hidden; transform-origin: 50% 100% 0; } Позиция inited:
custom-viewport[data-mode = "inited"] { transform: translateY(calc(100% - 50vh)); transition: transform 1s; }Позиция opened:
custom-viewport[data-mode = "opened"] { transform: translateY(0); transition: transform 1s; overflow-y: scroll; }Позиция deleted:
custom-viewport[data-mode = "deleted"] { transform: translateY(100%); transition: transform 1s; }Шаг 2 — начинаем писать компонент custom-viewport
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); } } Реализуем события dragUp/dragDown
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); } connectedCallback() { this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => { this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0]; }); this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => { this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY; return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown(ev) : this.dragUp(ev); }); } dragUp(ev) {} dragDown(ev) {} } Схематично код выше можно описать так
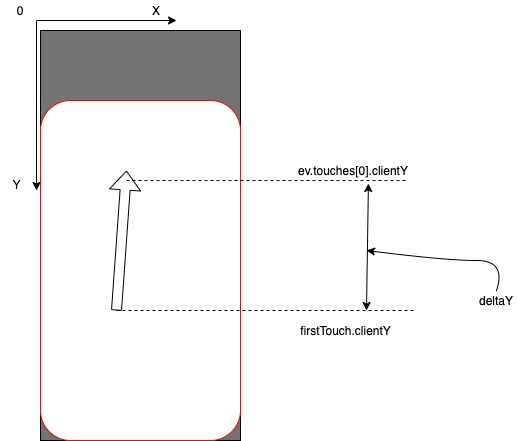
Итак, теперь мы умеем различать события dragUp/dragDown. Следующая утилита — расчет запаса хода.
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight; // + } connectedCallback() { this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => { this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0]; const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect(); // + const { height, top } = rect; // + this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT; // + }); this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => { this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY; return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown() : this.dragUp(); }); } dragUp() {} dragDown() {} isBottomOffset() { // + return (this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging + this.deltaY) > 0; // + } // + } Здесь мы сначала запоминаем сколько у нас было запаса хода на момент начала движения, а потом просто добавляем к этому значению deltaY и смотрим: можем мы двигаться вверх или нет.
Собственно логика dragUp:
... dragUp() { if(this.isBottomOffset()) { // переместить вверх return; } this.style.transform = 'translateY(0)'; } ... Пишем метод, который будет перемещать вьюпорт:
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight; } connectedCallback() { this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => { this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0]; const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect(); const { height, top } = rect; this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT; this.lastPosY = this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging - this.scrollTop; // + }); ... } translateY() { // + const pixels = this.deltaY + this.lastPosY; // + this.style.transform = `translateY(${pixels}px)`; // + this.style.transition = 'none'; // + } // + ... } Разберем поподробнее что такое this.lastPosY и как он высчитывается. Если в css мы писали transform: translateY(calc(100% — 50vh)); где 100% — это высота самого виртуального вьюпорта, а 50vh — это половина высоты реального вьюпорта, и для статического описания положения это подходит хорошо, то для вычисления перемещения в динамике удобнее оперировать абсолютными величинами, именно эти преобразования мы здесь производим.
Итак this.lastPosY — это величина перемещения виртуального вьюпорта в пикселях на момент начала движения, именно к нему мы добавляем this.deltaY и получаем новое положение вьюпорта.
Так как мы определили свойства:
bottom: 0; transform-origin: 50% 100% 0; то наша система координат для отсчета передвижения вьюпорта примет вид

Опишем dragDown:
... dragDown() { if(this.lastPosY < 0) { return; } this.translateY(); } ... Собственно событие dragEnd:
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight; } connectedCallback() { this.addEventListener("touchend", ev => { // + const { mode: currentMode } = this.dataset; // + this.style = null; // + if (Math.abs(deltaY) < 10) { // + this.dataset.mode = currentMode; // + return; // + } // + if (deltaY > 0) { // + if (currentMode === "inited") { // + this.dataset.mode = "deleted"; // + return; // + } // + this.dataset.mode = "inited"; // + return; // + } // + this.dataset.mode = "opened"; // + }); // + ... В строчке if (Math.abs(deltaY) < 10) мы указываем что если передвинулись меньше чем на 10 пикселей — оставить текущее положение.
В итоге у нас должен получиться компонент наподобие
class CustomViewport extends HTMLElement { constructor() { super(); this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = window.innerHeight; } connectedCallback() { this.addEventListener("touchstart", ev => { this.firstTouch = ev.touches[0]; const rect = this.getBoundingClientRect(); const { height, top } = rect; this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging = (height + top) - this.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT; this.lastPosY = this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging - this.scrollTop; }); this.addEventListener("touchmove", ev => { this.deltaY = ev.touches[0].clientY - this.firstTouch.clientY; return this.deltaY > 0 ? this.dragDown() : this.dragUp(); }); this.addEventListener("touchend", ev => { const { mode: currentMode } = this.dataset; this.style = null; if (Math.abs(this.deltaY) < 10) { this.dataset.mode = currentMode; return; } if (this.deltaY > 0) { if (currentMode === "inited") { this.dataset.mode = "deleted"; return; } this.dataset.mode = "inited"; return; } this.dataset.mode = "opened"; }); } dragUp() { if(this.isBottomOffset()) { this.translateY(); return; } this.style.transform = 'translateY(0)'; } dragDown() { if(this.lastPosY < 0) { return; } this.translateY(); } translateY() { const pixels = this.deltaY + this.lastPosY; this.style.transform = `translateY(${pixels}px)`; this.style.transition = 'none'; } isBottomOffset() { return (this.bottomOffsetBeforeDragging + this.deltaY) > 0; } } customElements.define('custom-viewport', CustomViewport); Данный код не является законченной реализацией, а лишь прототипом. Более детальная проработка скрола, дебоунсы, еще какие-либо оптимизации, touchcancel — оставлены на откуп читателю.
ссылка на оригинал статьи https://habr.com/ru/post/500254/
Добавить комментарий